Comparing Advanced Peptide-Based Treatments for Medical Weight Loss
Comparing Advanced Weight Loss Injections: A Guide to Choosing the Right Option
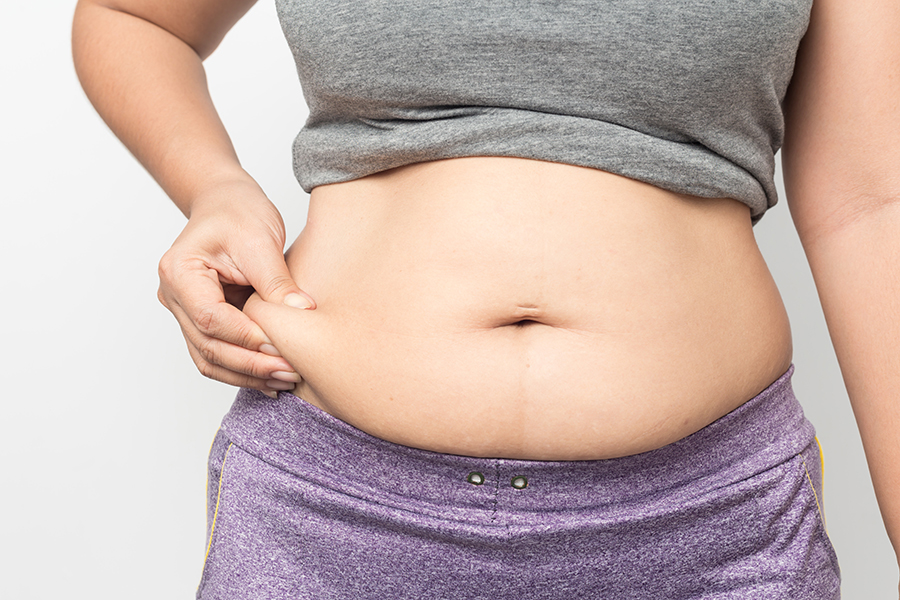
In recent years, innovative injectable medications have emerged as effective tools for individuals seeking sustainable weight loss support. These treatments are designed to help manage appetite, improve metabolic function, and promote consistent fat reduction—all with the convenience of once-weekly or daily administration. In this guide, we’ll explore two types of advanced weight loss injections, comparing how they work, how they’re administered, and what results you can expect.
Mechanism of Action
Weight Loss Injections (Type A):
These injections work by targeting receptors in the brain that regulate hunger and satiety. They help increase feelings of fullness, reduce appetite, and slow down digestion. This can result in lower calorie intake, improved eating habits, and gradual weight reduction over time.
Weight Loss Injections (Type B):
This newer formulation goes a step further by activating multiple biological pathways involved in metabolism and appetite regulation. The dual mechanism of action enhances blood sugar balance while also reducing cravings and supporting more significant weight loss compared to single-pathway treatments.
Clinical Results and Effectiveness
Type A Injections:
These have been widely studied and have shown consistent success in clinical trials, with many individuals achieving weight loss of 15% or more when used alongside a structured lifestyle program. Participants also reported improved eating behaviors and better portion control.
Type B Injections:
Clinical trials for this newer injection type have shown even more dramatic improvements in both weight loss and metabolic markers. Participants often achieved results equal to—or greater than—those using single-pathway medications, making this an appealing option for individuals with more significant weight loss goals.
Dosing and Administration
Type A Injections:
These are typically administered once per week via a subcutaneous autoinjector. Dosing usually begins conservatively and is gradually increased based on individual tolerance and weight loss progress.
Type B Injections:
This formulation is also administered subcutaneously and is available in both weekly and daily formats. It begins with a low dose and is titrated upward depending on your response and your healthcare provider’s recommendation.
Possible Side Effects
As with any medication, side effects may occur. Common symptoms for both injection types include mild gastrointestinal discomfort such as nausea, bloating, or diarrhea—especially during the initial adjustment period. These effects tend to diminish over time and can often be managed by adjusting the dosage or schedule. It’s important to work closely with a provider to monitor your progress and comfort.
Final Thoughts
Both types of weight loss injections represent powerful advancements in medical weight management. While one may be better suited for your goals, lifestyle, or body chemistry, both are best used as part of a comprehensive plan that includes healthy nutrition, physical activity, and ongoing support. A consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is the best way to determine which option aligns with your unique needs.
With the right strategy and consistent care, these modern tools can help unlock lasting, transformative results in your weight loss journey.